How Do Calcium Ions Move Across the Cell Membrane
Amino acids glucose and other large membrane insoluble compounds move through the cell membrane through a process known as facilitated diffusion. They are responsible for the transmembrane potential and thus the functioning of the cell.
The Action Potential Anatomy And Physiology
To recover from a contraction Ca2 pumps in the sarcoplasmic reticulum must consume ATP to remove Ca2 from the cytosol.

. Calcium ions cannot move across a cell membrane by simple diffusion. They are mostly caused by mutations in genes that code for the ion channels. Each phospholipid molecule contains a phosphate head and two lipid or fatty tails.
Secondary active transport describes the movement of material that is due to the electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport that does not directly require ATP. Keeping this in consideration do calcium ions move across a cell membrane by simple diffusion. I thought the process was.
These channels basically regulate the Dynamics of the cell. This process involves transmembrane proteins which open up a small water-filled channel through which the molecules can pass into or out of the cell. Active diffusion is when molecules move through a selectively permeable membrane from an area of low to high concentration.
Passive mechanisms like diffusion use no energy while active transport requires energy to get done. Meanwhile for some types of calcium channels potential-dependent activation analogous to that in sodium or potassium channels is observed. Usually this happens when the cell is moving ions against the established gradient like moving water uphill.
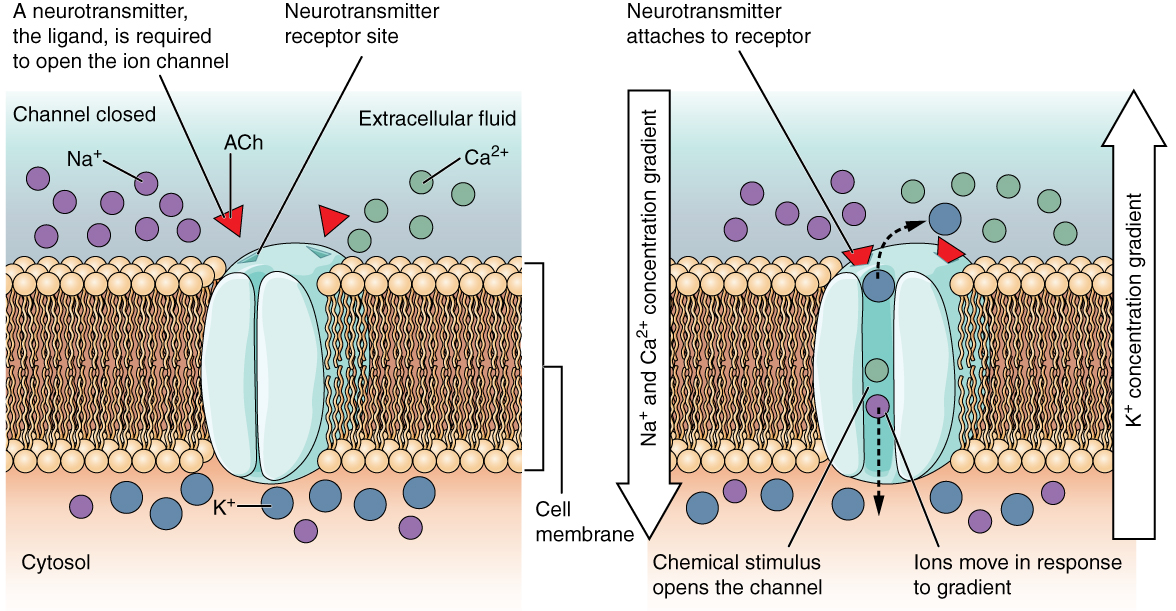
The ligand is often external neurotransmitter or hormone or internal intracellular Ca cAMP. Because calcium is positively charged it cant freely cross the plasma membrane because that structure is composed of Phospholipids molecules with a polar head and non-polar tail. A concentration gradient exists that would allow ions and polar molecules to diffuse into the cell but these materials are repelled by the hydrophobic parts of the cell membrane.
Cell membranes have what is known as an electrochemical gradient across the phospholipid bilayer of the membrane. Sometimes the cell uses special machinery to transport the ions across the membrane as well though so in this case there is flow because the cell directs it. Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane which is directly dependent on ATP.
This means that ions like sodium potassium calcium and chloride cannot cross membranes to any significant degree by simple diffusion and must instead be transported by specialized proteins which well discuss later. Calcium exists as a gradient across the plasma membrane wherein the extracellular concentrations. Calcium Ca2 plays a significant role in cell signaling.
The phosphates form the membranes inner and outer boundaries while the lipid tails occupy the space in between. During long-term membrane depolarization the calcium channels pass into an inactivated state which is connected with the recurrent blocking action of calcium ions entering the cell on the channels. Movement Across a Membrane and Energy.
Cartoon representing passive transport as rolling a boulder. The cell membrane is not very permeable to sodium ions so they must enter through a process known as facilitated diffusion. This gradient is maintained by protein pumps embedded in the membrane that move some types of ions charged particles across the membrane in one direction while similar pumps move other types of ions in the opposite direction leading to a.
View the full answer. Why cant Na Cross plasma membrane. There are two major ways that molecules can be moved across a membrane and the distinction has to do with whether or not cell energy is used.
Active diffusion requires carrier proteins and cellular energy. Normally small non-polar and hydrophobic molecules are able to enter and pass through the cells bi-lipid membrane however the permeability to ions is very low due to. In facilitated diffusion sodium passes through the cell membrane in a voltage-gated ion channel which is opened by a change in electrical current across the membrane.
Facilitated diffusion uses integral membrane proteins to move polar or charged substances across the hydrophobic regions of the membrane. They lead to redundancy of cellular functions because the ion channels are what made the cell dynamic. 2 the cell membrane invaginates and reaches around the protein enveloping it.
When a muscle cell is stimulated Ca2 pumps in the sarcoplasmic reticulum use the energy of ATP to move Ca2 into the cytosol stimulating the cell to contract. This tail doesnt allow the passage of ions. The lipids are hydrophobic meaning they repel water and substances dissolved in water such as sodium.
The cell membrane is composed of a double layer of phospholipids. 3 the cell membrane having surrounded the protein pinches off creating an intracellular vesicle containing the protein. 1 some extracellular substance say a protein binds with a receptor on the cells membrane.
Other transport proteins are carriers that bind ions and other molecules and then change their configuration moving the bound molecule from one side of the cell membrane to the other.
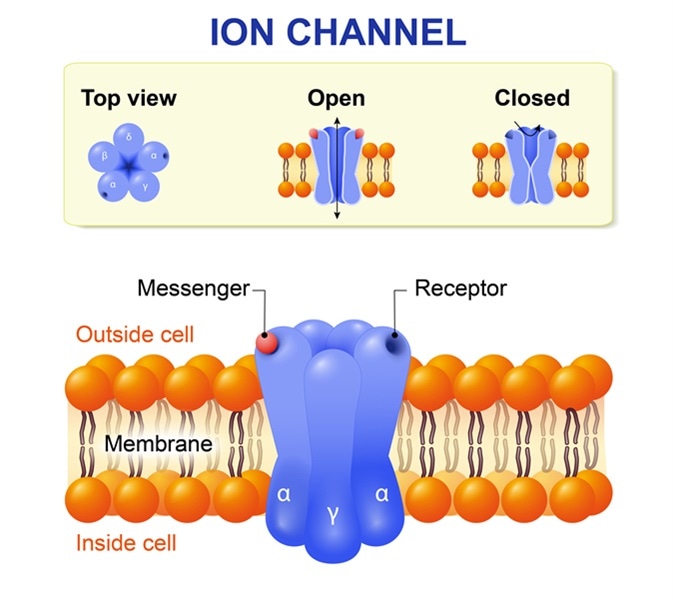
Types Of Ion Channels In The Body

Membrane Channel Types Human Physiology Openstax Cnx

The Plasma Membrane Calcium Pump New Ways To Look At An Old Enzyme Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Comments
Post a Comment